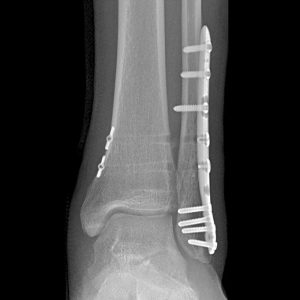
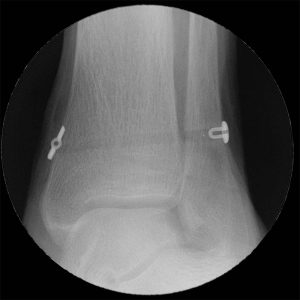
Ankle Syndesmosis Repair System with Acu-Sinch® Knotless
Overview
The tibiofibular syndesmosis is disrupted in approximately 10–20% of ankle fracture cases and requires repair.1,3 For decades, screw fixation of the syndesmosis has been the gold standard for treatment.1 However, emerging clinical evidence has demonstrated that flexible, suture-based syndesmosis repairs have successful clinical outcomes and may reduce complications associated with malreduction of the syndesmosis when fixed with screws.2,3,4
Designed in conjunction with Alastair Younger, MB, Ch.B., M.Sc., Ch.M., FRCS(C); Selene Parekh, MD, MBA; and Steven Morgan, MD, the Acu-Sinch Knotless Implant enables the dynamic stabilization of laxity or syndesmotic disruptions to the tibiofibular joint.
The Acu-Sinch Knotless buttons may be augmented with a washer or may be used in conjunction with the Acumed and OsteoMed® fibula fracture fixation plates and intramedullary nails with 3.5mm nonlocking screw holes. Our patent pending release mechanism gives the user control to place the medial button subcutaneously without the need for direct visualization.
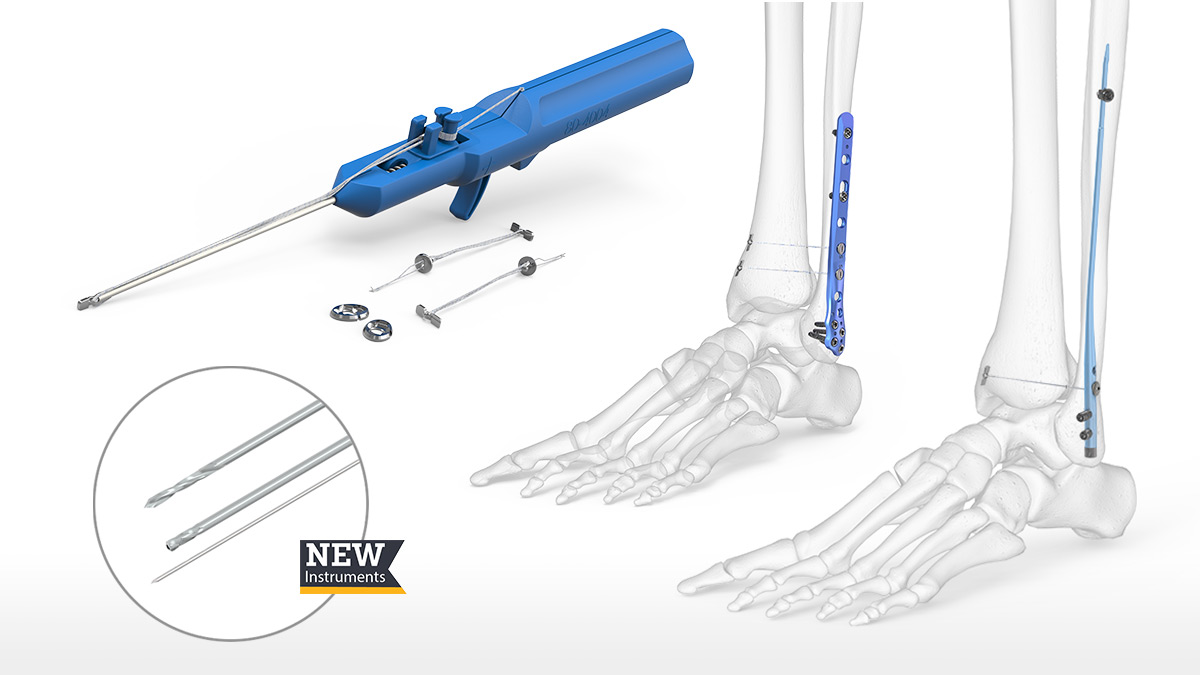
New optional instrumentation aimed to provide predictable outcomes and procedural efficiency: A 3.5 mm Cannulated Drill and 1.3 mm K-wire allows the surgeon to confirm the trajectory prior to drilling and a 3.5mm Long Drill and Drill Guide provides single-step drilling for Acu-Sinch Knotless through the Fibula Nail 2.
Related Documents
Ankle Syndesmosis Repair System with Acu-Sinch Knotless Procedures
The Ankle Syndesmosis Repair System with Acu-Sinch Knotless can be used in the following procedures:
Syndesmosis Injury (Ankle), Acromioclavicular Joint Separation (Clavicle), Clavicle Fracture (Clavicle)Key Features
Dynamic Stabilization
Suture-based dynamic ankle syndesmosis stabilization.
Unique Inserter
Unique inserter for implant deployment without a medial incision.
Integrated
Integrates with Acumed and Osteomed fibula fracture fixation products.
Streamline Your Flexible Syndesmotic Cases
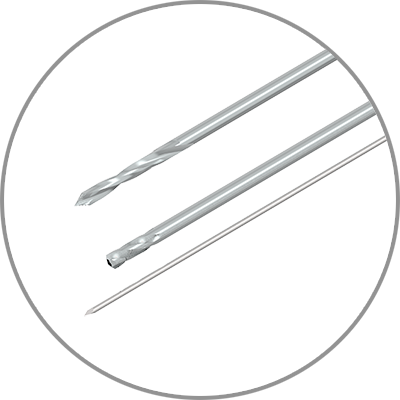
New optional instrumentation aimed to provide predictable outcomes and procedural efficiency include A 3.5 mm Cannulated Drill and 1.3 mm K-wire allowing the surgeon to confirm the trajectory prior to drilling, and a 3.5 mm Long Drill and Drill Guide providing single-step drilling for Acu-Sinch Knotless through the Fibula Nail 2.
Drill Options
Videos
Images
References
- Schepers T. Acute distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury: a systematic review of suture-button versus syndesmotic screw repair. Int Orthop. 2012;36(6):1199-1206. doi:10.1007/s00264-012-1500-2
- Raeder B, Figved W, Madsen J, Frihagen F, Jacobsen S, Andersen M. Better outcome for suture button compared with single syndesmotic screw for syndesmosis injury: five-year results of a randomized controlled trial. Bone Joint J. 2020;102- B(2):212-219. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.102B2.BJJ-2019-0692.R2.
- Shimozono Y, Hurley E, Myerson C, Murawski C, Kennedy J. Suture Button Versus Syndesmotic Screw for Syndesmosis Injuries A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Sports Med. 2019 Sep;47(11):2764-2771. doi:10.1177/0363546518804804
- Laflamme M, Belzile E., Bédard L, van den Bekerom M, Glazebrook M, Pelet S. A prospective randomized multicenter trial comparing clinical outcomes of patients treated surgically with a static or dynamic implant for acute ankle syndesmosis rupture. J Orthop Trauma 2015; 29(5): 216-223.