Ankle Plating System 3
March 27, 2018
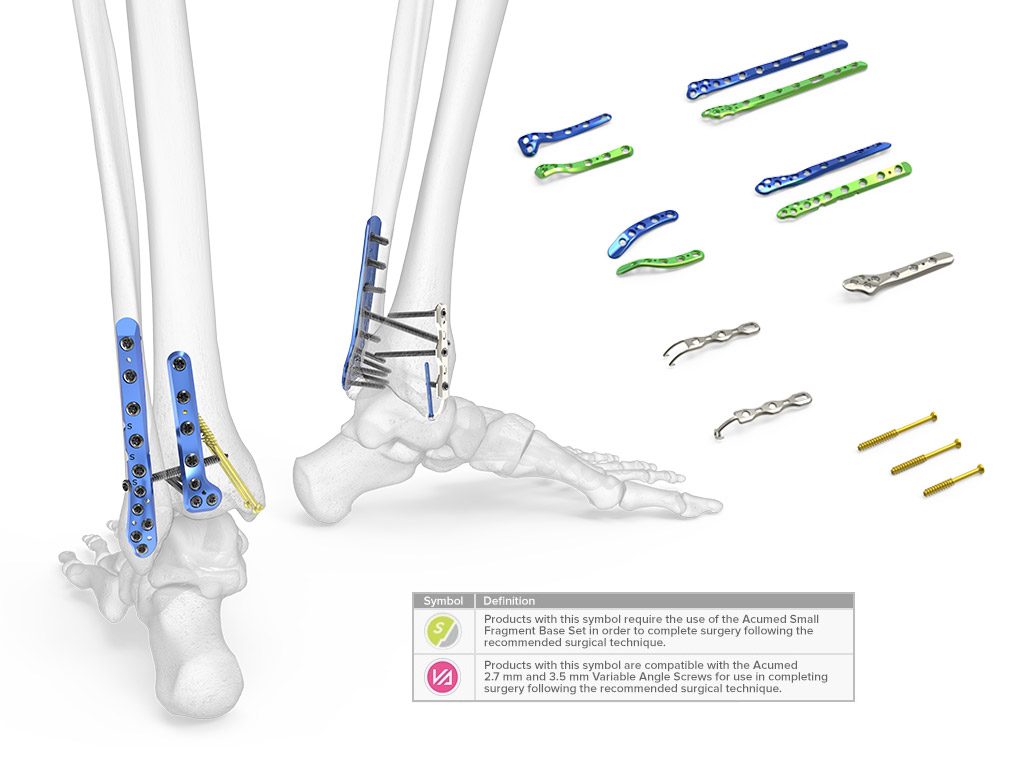
The Acumed Ankle Plating System 3 is designed to provide a variety of fixation options for fractures of the distal tibia and fibula. Designed in conjunction with Anish Kadakia, M.D. and Bruce Ziran, M.D., the system is composed of seven plate families designed specifically for the treatment of ankle fractures. The indication-specific plates address fracture patterns of the medial, lateral, and posterior malleoli. Specialized plate features and unique instrumentation address disruption of the syndesmosis. 4.0 mm cannulated screws in lengths of 36 mm, 42 mm, and 48 mm are also included in the tray for the treatment of medial malleolar fractures.
Product Overview
The Acumed Ankle Plating System 3 is designed to provide a variety of fixation options for fractures of the distal tibia and fibula. Designed in conjunction with Anish Kadakia, M.D. and Bruce Ziran, M.D., the system is composed of seven plate families designed specifically for the treatment of ankle fractures.
The indication-specific plates address fracture patterns of the medial, lateral, and posterior malleoli. Specialized plate features and unique instrumentation address disruption of the syndesmosis. 4.0 mm cannulated screws in lengths of 36 mm, 42 mm, and 48 mm are also included in the tray for the treatment of medial malleolar fractures.
The Ankle Plating System 3 is used in combination with the Acumed Small Fragment Base Set. The Small Fragment Base Set includes One-Third Tubular Plates, as well as cut-to-length and bend-to-fit 2.7 mm L-shaped, T-shaped, and straight Fragment Plates that can also be used to address ankle fractures.
The 2.7 mm and 3.5 mm locking, nonlocking, and variable angle hexalobe screws, 4.0 mm fully threaded and partially threaded cancellous hexalobe screws, and universal instrumentation are all housed in the Small Fragment Base Set. A selection of Tension Band Pins and AcuTwist Compression Screws are also included in the tray.
Features
- The First Fragment-Specific Posterior Distal Tibia Plates on the Market:
With 67% of posterior malleolus fractures involving the lateral corner,8 Acumed offers fragment-specific plates anatomically contoured to fit each side of the posterior malleolus and to capture comminution at the articular surface. - Thin Lateral Fibula Plates:
Designed to minimize soft tissue irritation, these plates are thinner both distally and proximally than DePuy Synthes, Arthrex, and Zimmer Biomet Lateral Fibula Plates.9 - Two Styles of Hook Plates:
These plates can be placed on either the lateral or medial malleolus. The Locking Peg Hook Plate includes a 2.3 mm Locking Cortical Peg across the fracture side for added support, and the fracture can be compressed and held in place with the Hook Plate Reduction Handle. - Two Plates, One Incision:
A single incision is possible for both the Posterolateral Fibula and Posterolateral Distal Tibia plates to address a trimalleolar ankle fracture.
Innovative Instrumentation
The Syndesmosis Targeting Guide, uniquely developed by Acumed, attaches to the Posterolateral Fibula Plates and allows the surgeon to target the desired angle for syndesmotic screw fixation.
Published literature has shown that the target location for syndesmosis screw fixation should be at the center of the tibia, through the fibula, 1 to 3 centimeters above the tibial plafond.1,3,4
Small Fragment Base Set
The Ankle Plating System 3 is used in combination with the Acumed Small Fragment Base Set, a comprehensive system for small fragment trauma surgeries of the upper and lower extremities.
The set is designed as both a stand-alone system with traditional plating as well as a complement to Acumed’s precontoured, anatomic-specific plating systems such as the Ankle Plating System 3.
Screws in the system include 2.7 and 3.5 mm locking, nonlocking, and variable angle hexalobe screws, as well as 4.0 mm fully and partially threaded cancellous hexalobe screws. The system also features straightforward instrumentation including fragment plate benders, fragment plate cutters, and a variety of drills and drill guides.
Posterior Malleolus Fracture Fixation
Published literature suggests that ankle fractures with involvement of the posterior malleolus are both underestimated and underdiagnosed.5 Fractures involving the posterior malleolus lead to poorer outcomes even when the fragment is small,6 with outcomes that may be worse with larger fragments.7
The Ankle Plating System 3 incorporates 4.0 mm cannulated and cancellous screws, one-third tubular plates, fragment plates, and unique plating options for both the posteromedial and posterolateral distal tibia to specifically address these difficult fracture patterns.
Posterior Malleolus Fracture Fixation
Published literature suggests that ankle fractures with involvement of the posterior malleolus are both underestimated and underdiagnosed.5 Fractures involving the posterior malleolus lead to poorer outcomes even when the fragment is small,6 with outcomes that may be worse with larger fragments.7
The Ankle Plating System 3 incorporates 4.0 mm cannulated and cancellous screws, one-third tubular plates, fragment plates, and unique plating options for both the posteromedial and posterolateral distal tibia to specifically address these difficult fracture patterns.
Seven Indication-Specific Plate Families
The seven plate families in the Ankle Plating System 3 address fracture patterns of the medial, lateral, and posterior malleoli:
- Lateral Fibula Plate (7 lengths, left and right specific): The Lateral Fibula Plates include two plate holes labeled with an ‘S’ which have a fixed 30 degree anterior angle to target the center of the tibia to help optimize syndesmosis screw positioning.1,2
- Posterolateral Fibula Plate (5 lengths, left and right specific): The Posterolateral Fibula Plates sit under the peroneal tendons and contain three scallops labeled with an ‘S’ that allow for syndesmosis screw fixation adjacent to the plate, targeted between 1 cm and 3 cm above the tibial plafond. The scallops may be targeted freehand or with the adjustable Syndesmosis Targeting Guide included in the set.
- Posterolateral Distal Tibia Plate (2 lengths, left and right specific): The Posterolateral Distal Tibia Plates incorporate a unique contour designed to act as a template and to aid in anatomic fracture reduction. The plates also include a distal cluster of 2.7 mm hexalobe screws that are angled approximately 15 degree superior to the joint space.
- Posteromedial Distal Tibia Plate (1 length, left and right specific): The Posteromedial Distal Tibia Plate sits beneath the posterior tibial tendon and is designed with a low plate and screw profile. The distal end of the plate is contoured and is designed to act as a buttress to distal fragments. The two distal 2.7 mm hexalobe screws are angled with the intention to avoid the joint space.
- Medial Anti-Glide Plate (1 length): The Medial Anti-Glide Plate is designed to address vertical shear fractures of the medial malleolus. This plate functions similarly to a one-third tubular plate but is more contoured and includes a distal cluster of 2.7 mm hexalobe screws to capture fragments in cases with distal comminution.
- Hook Plate (2 lengths): The two prongs at the distal end of the Hook Plate are designed to support an avulsion fragment when the fragment may be too small for a lag screw. The Hook Plates may be placed on either the lateral or medial malleolus.
- Locking Hook Plate (2 lengths): The Locking Peg Hook Plates are designed to support an avulsion fragment that may require additional stability and include a 2.3 mm Cortical Peg through the distal end of the plate for additional support. The Locking Peg Hook Plates may be placed on either the lateral or medial malleolus.
4.0 mm Cannulated Screws
4.0 mm cannulated screws are included in the Ankle Plating System 3 tray in lengths of 36 mm, 42 mm, and 48 mm.
Additional lengths of 4.0 mm cannulated screws — short thread (1/3 threaded) from 10 mm-72 mm and long thread (1/2 threaded) from 16 mm-72 mm — are housed in the standalone 4.0 mm Cannulated Screw Caddies tray and use the instruments within the Ankle Plating System 3.
Screws
The 2.7 mm and 3.5 mm locking, nonlocking, and variable angle hexalobe screws, 4.0 mm fully threaded and partially threaded cancellous hexalobe screws, and universal instrumentation are all housed in the Small Fragment Base Set. A selection of Tension Band Pins and AcuTwist Compression Screws are also included in the tray.
Citations
1. Needleman, RL. Accurate reduction of an ankle syndesmosis with the ‘glide path’ technique. Foot Ankle Int. 2013;34:1308-1311.
2. Van den Bekerom M, Hogervorst M, Bolhuis CN. Operative aspects of the syndesmotic screw: Review of current concepts. Injury. 2008;39:491-498.
3. Barbosa, P, Bonnaire, F, Kojima, K. Fibulo-tibial positioning screw. AO Foundation website. Published December 4, 2006.
4. Wheeless, C. Technique of syndesmotic fixation. Wheeless Textbook of Orthopaedics website. Published December 11, 2014.
5. Switaj P, Weatherford B, Fuchs D, Rosenthal B, Pang E, and Kadakia AR. Evaluation of posterior malleolar fracturesand the posterior pilon variant in operatively treated ankle fractures. Foot Ankle Int. Published online June 18, 2014.
6. Jaskulka RA, Ittner G, Schedl R. Fractures of the posterior tibial margin: their role in the prognosis of malleolar fractures. J Trauma. 1989;29:1565-1570.
7. Broos PL, Bisschop AP. Operative treatment of ankle fractures in adults: correlation between types of fracture and final results. Injury. 1991;22: 403-406.
8. Haraguchi et al. Pathoanatomy of Posterior Malleolar Fractures of the Ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:1085-92.
9. Internal document on file.
